The high-temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR), which is graphite-moderated and helium-cooled, is attractive due to its unique capability of producing high temperature helium gas and its fully inherent reactor safety. In particular, hydrogen production using the nuclear heat from HTGR (900°C and higher) offers one of the most promising technological solutions to curb the rising level of CO2 emission and resulting risk of climate change.
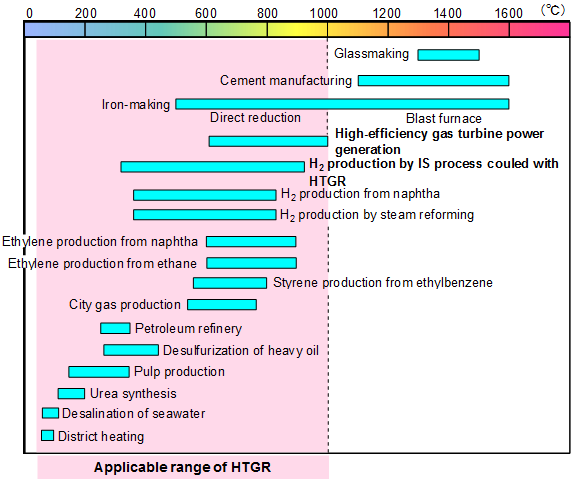
The nuclear heat from HTGR also can be used for other industrial fields such as high-efficiency gas-turbine power generation, ethlene production, pulp production, sesalination of seawater, district heating etc.
The interests in HTGR as an advanced nuclear power source for the next generation reactor, therefore, continue to rise. To enhance nuclear energy application to heat process industries, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has continued extensive efforts for development of hydrogen production system using the nuclear heat from HTGR in the framework of the HTTR Project. The HTTR Project has the objectives of establishing both HTGR technology and heat utilization technology.
FAQ
- What is HTGR ?
- Structure of HTGRs
- Temperature Ranges Applicable to Various Industrial Fields
- Development Status of HTGRs in the World
- Outline of High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor
- Establishment of technical bases of high temperature gas-cooled reactor with the HTTR
- Various Hydrogen Production Methods
- R&D on Thermochemical IS Process
- Hydrogen Society in the Future