Waste and Environmental Safety Research Group
In order to provide the technical and scientific information on safety management of radioactive wastes, we have been developing the safety assessment methods for decommissioning of nuclear facilities and for disposal of radioactive waste including contaminants generated from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear facility accident.
The objective of our research is to improve the methods of both long-term performance assessment models for barrier materials with safety functions and safety assessment models for waste disposal and decommissioning.
Our group is promoting research on the following three themes in cooperation with the Nuclear Regulatory Authority and related organizations inside and outside.
- Research on safety and performance assessment in radioactive waste disposal
- Research on safety assessment for decommissioning of nuclear facilities
- Research on scientific basis for future decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
Ⅰ.Research on safety and performance assessment in radioactive waste disposal
(1) Natural barriers
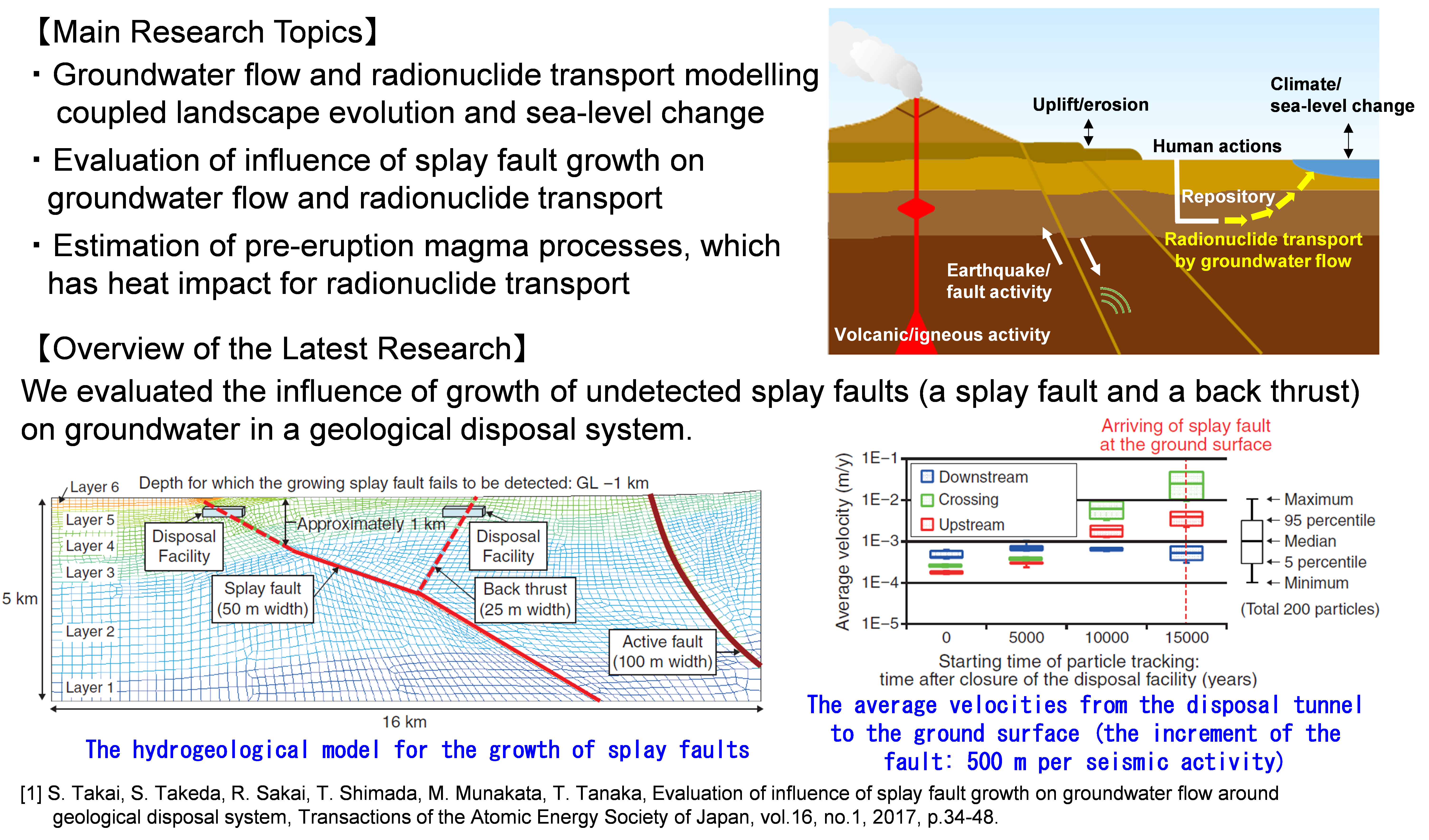
Natural barriers consist of the geological media hosting the repository, and any other geological formations. The functions of natural barriers are to isolate the wastes from humans and the environment and to impede migration from disposal facilities (low groundwater flow, sorption, reducing condition). In the safety assessment for more than tens of thousands years, natural phenomena which could adversely influence the functions need to be considered. We have developed scientific and technical knowledge for the influence of natural phenomena.
(2)Engineering barriers
●Bentonite
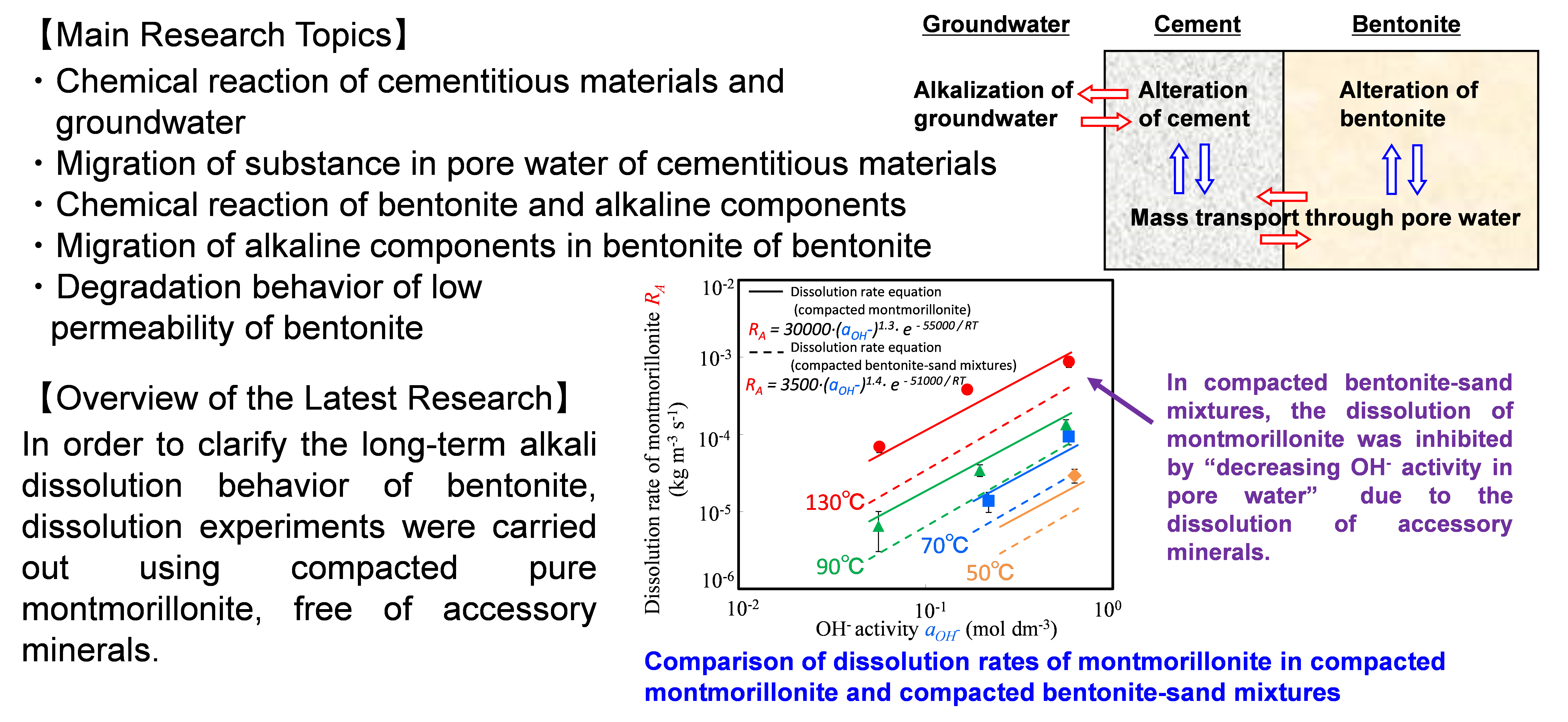
In disposal systems of radioactive waste, compacted bentonite is a candidate as an engineering barrier material. It is expected to retard the migration of radionuclides from the waste packages with its low permeability. However, highly alkaline groundwater, which can be generated from the dissolution of cementitious material in the system, is likely to dissolve montmorillonite (the main constituent of bentonite), declining physical and/or chemical functions of the barrier material. Therefore, we are developing scientific and technical knowledge on the mineralogical alteration by bentonite-cement interactions (mineral reaction) and the accompanying changes in mass transport properties in order to judge the validity of the performance evaluation for the bentonite barrier by the disposal operators.
●Cementitious Materials
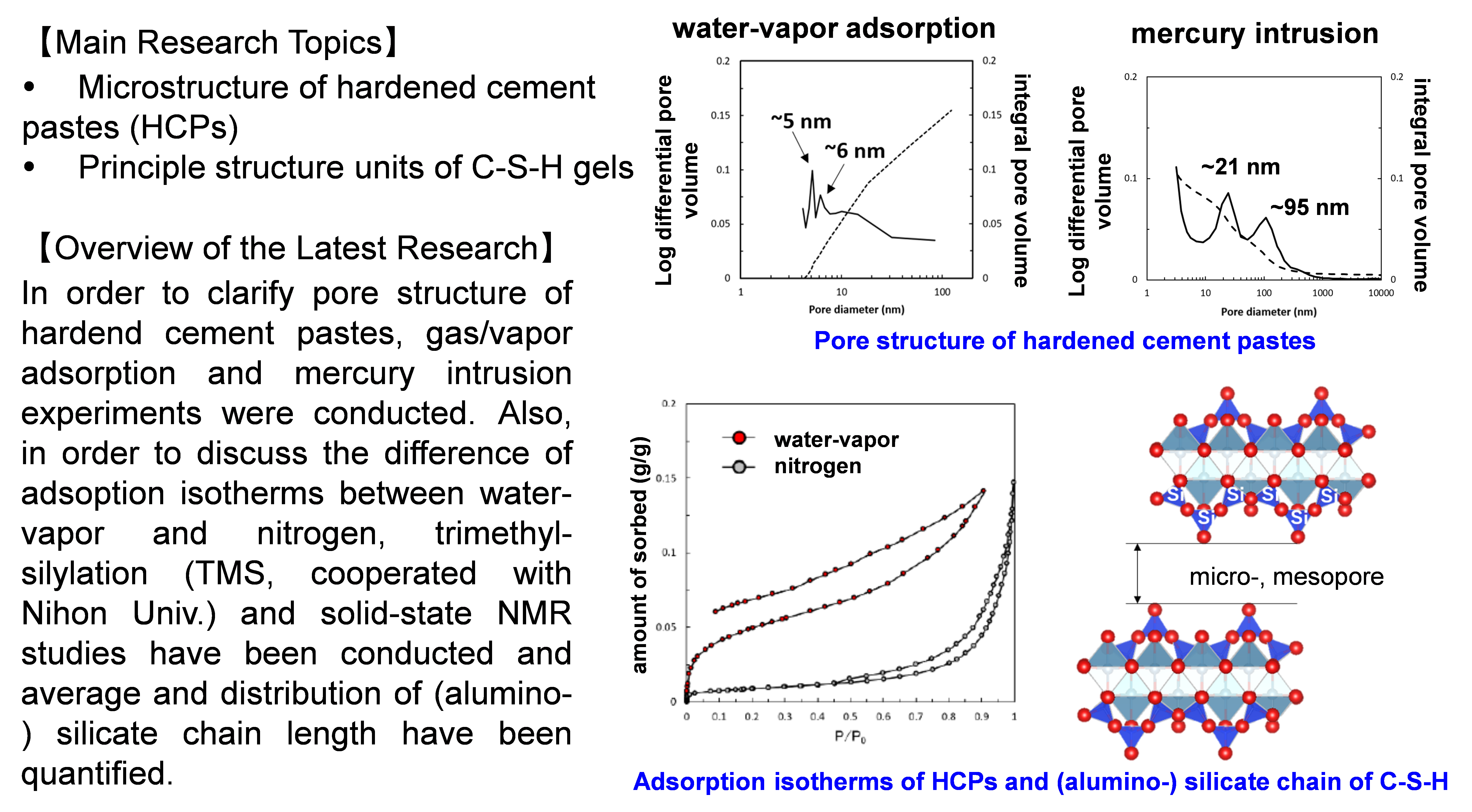
In disposal systems of radioactive waste, cementitious materials are candidates as the engineering barrier. It is expected to retard the migration of radionuclides from the waste packages with low diffusivity and high sorptivity against radionuclides. We are developing scientific and technical knowledge on the micro- and mesopore of calcium silicate hydrate gels (= C-S-H), major component of cementitious materials, in order to judge the validity of the performance evaluation for the cementitious barrier by the disposal operators.
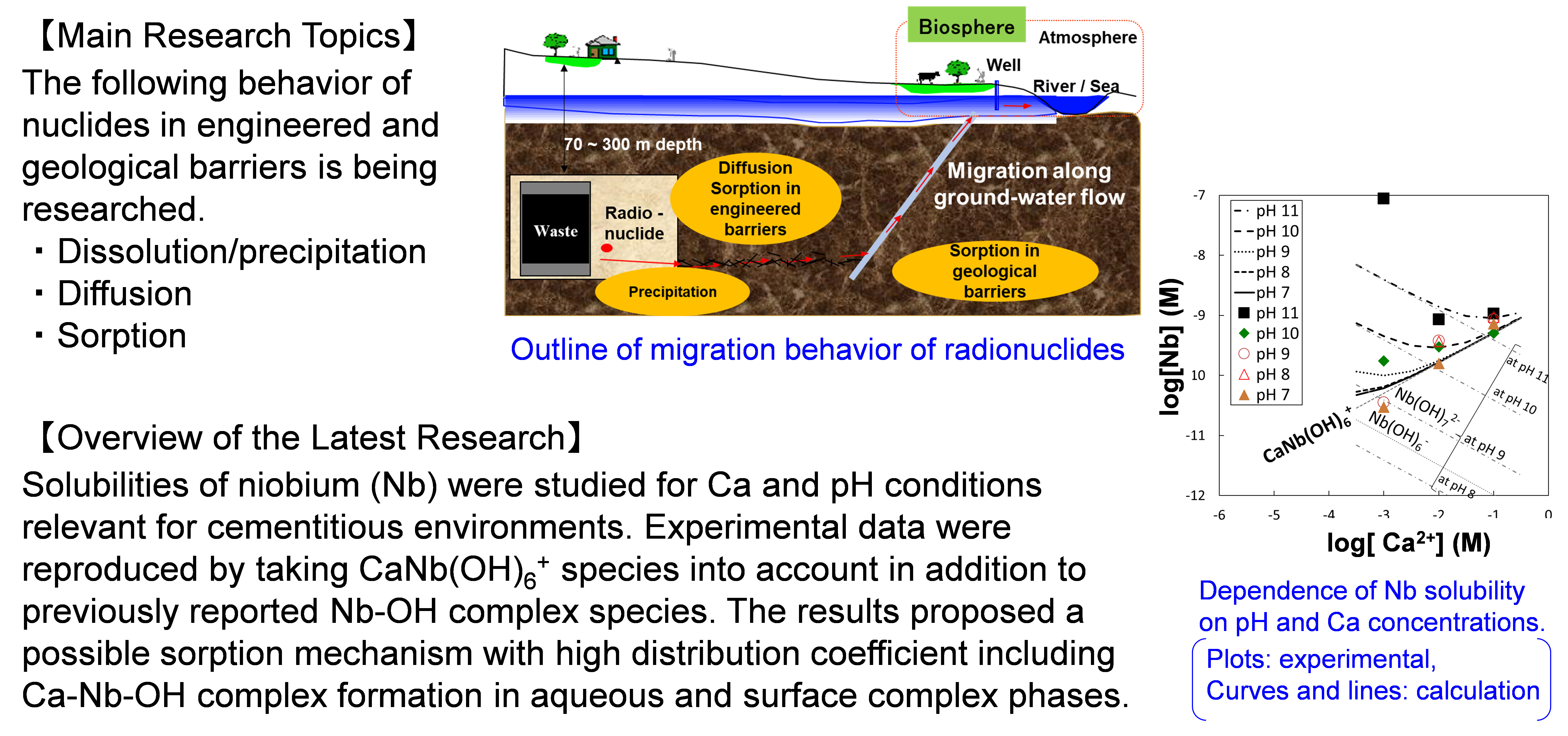
(3)Migration behavior of radionuclides
Radioactive waste disposal relies on a multi-barrier system to isolate the waste from biosphere. The system is constituted by engineered barriers and geological barriers. In order to estimate radiation dose of public, their retardation effects on radionuclide migration are estimated as migration parameters, for example, solubility, diffusion coefficient, and distribution coefficient.
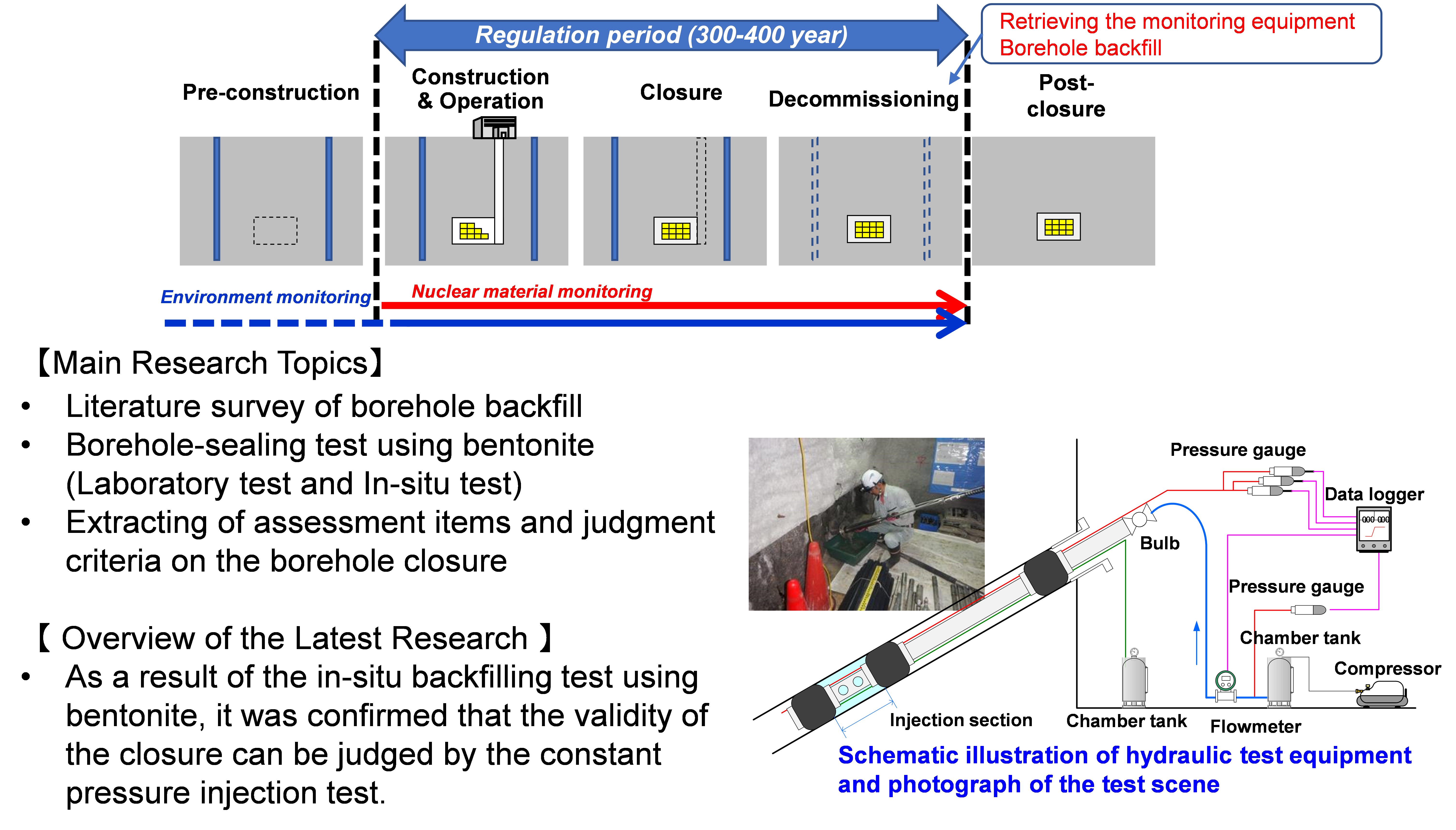
(4)Monitoring
The monitoring of radioactive material leakage is planned for the medium-depth disposal of type 2 radioactive waste in Japan. At the end of the monitoring period, the monitoring borehole will be backfilled with bentonite or sand to eliminate a potential water flow path. Therefore, we are developing scientific and technical knowledge on the borehole sealing in order to judge the validity of the borehole closure by the disposal operators.
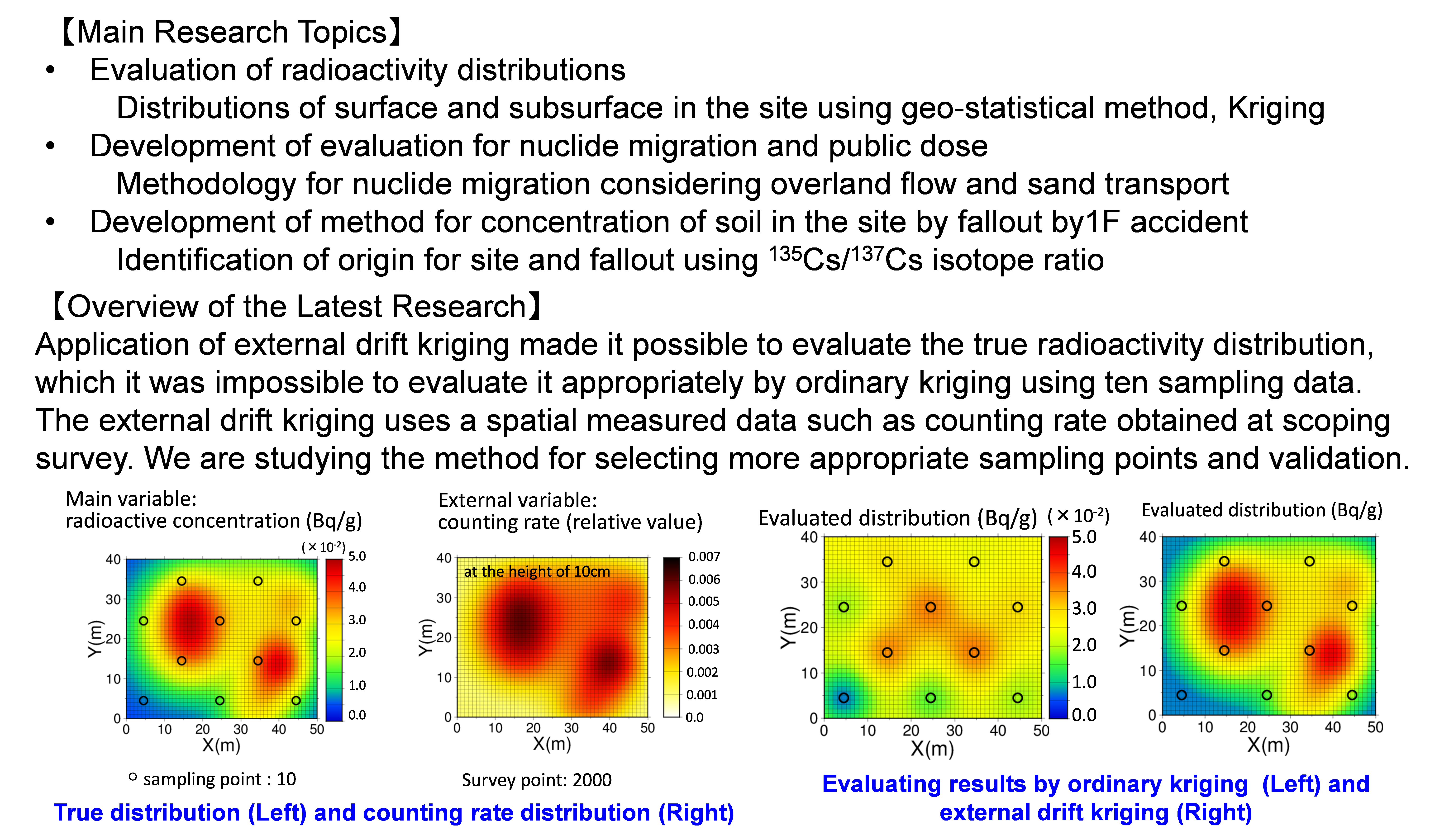
Ⅱ.Research on safety assessment for decommissioning of nuclear facilities
We are developing the methodology and code system for evaluating dose of public using the land after completion of decommissioning, based on the radioactivity distribution in the site to comply with dose criteria. The distribution will be changed by strong rain depending on the site character.
Ⅲ.Research on scientific basis for future decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
When radioactive wastes including the accidental waste of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station are disposed of in the repository sites, the inventory of the radionuclides in the wastes have to be evaluated. In order to validate the analytical value measured various analytical methods, applicable range of each method and technical points to note are summarized.
