R&D for disposal and storage of radioactive waste
For the determination of the processing, storage and disposal methods of the waste arising from the accident and radioactive adsorbents used for treatment of the contaminated water, it is necessary to investigate the characteristics of the waste. The characteristics of the waste are also important to understand the accident progression.
Safe storage of secondary waste from the contaminated water processing
◎ Objective
Radioactive cesium in the contaminated water in the reactor building is removed with the adsorption vessel filled with zeolite-like media. A Similar purification system with zeolites was employed in the case of the Three Mile Island accident. However, the behavior of zeolite used in a seawater system like the Fukushima case is not well understood.
The spent zeolite vessel adsorbing cesium is highly radioactive, and sampling of the used zeolite is difficult. Therefore, analysis and evaluation of its properties and characteristics with the simulated zeolite vessel are essential for the safety confirmation during storage, processing and disposal.
◎ R&D activities
The radiation dose from spent zeolite is too high to measure or examine its characteristics directly. Instead of direct measurements, miniature equipment is used to evaluate the zeolite characteristics (chemical composition, radioactivity, heat generation, etc.). A simulation code for radionuclides adsorption on zeolite is also developed to estimate the cesium concentration in the actual adsorption vessel.
The seawater might remain in the spent vessel after washing and affect the integrity of vessel material and hydrogen gas generation. Obtained fundamental data related to zeolite, seawater and radiation are analyzed in combination with results of full scale vessel tests to evaluate the rationality of the current storage method.
◎ Related facilities
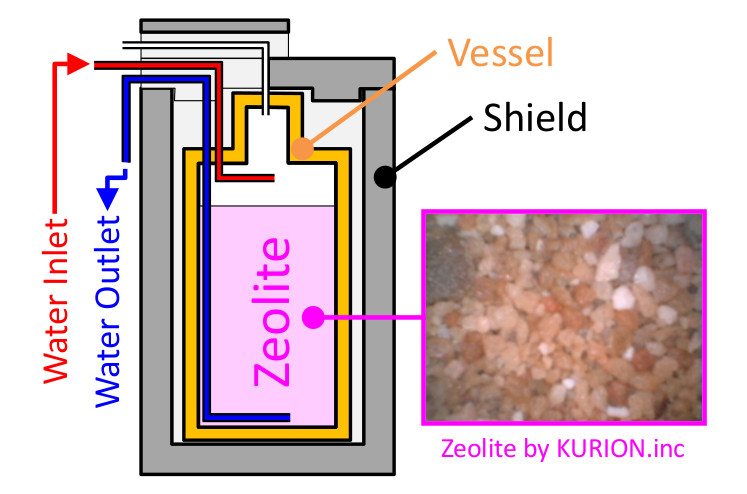
Cross section diagram of the adsorption vessel and shield
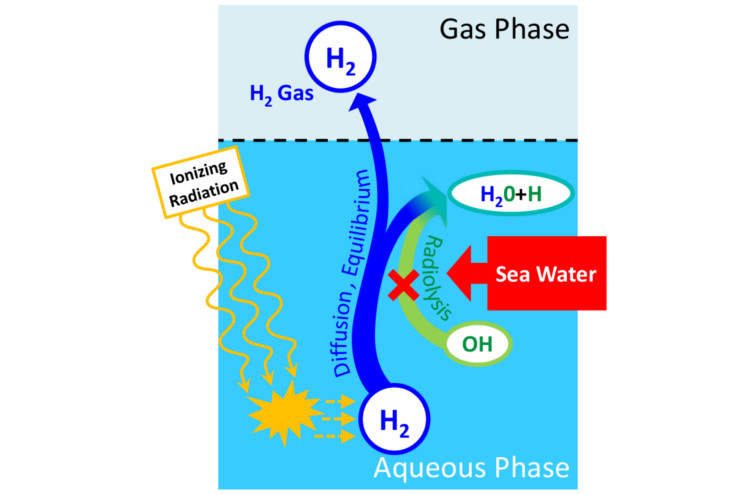
Mechanism of hydrogen generation by radiation from cesium
This R&D contributes to part of the "Mid-and-Long-Term Roadmap towards the Decommissioning of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Units 1-4".
- (3-1) Development of Technologies for the Processing and Disposal of Secondary Waste produced by the Processing of Contaminated Water
Characterization of primary waste
◎ Objective
Many kinds of waste, such as concrete, gravel and metal, were generated by the accident and they are contaminated with a wide variety of radionuclides. They must be processed and disposed of properly as radioactive waste.
To carry out processing and disposal of this waste, it is necessary to clarify the radionuclide inventory including the amount, kind, adherence condition, etc.
◎ R&D activities
The various kinds of waste sampled at Fukushima Daiichi NPP site are transferred to the Nuclear Science and Research Institute, JAEA for radiochemical analysis. These results are used for the development of processing and disposal techniques, and also provided to the other R&D teams regarding Fukushima NPP decommissioning project.
Additionally, new analytical techniques are being developed for fast and precise determination of the radioactivity. Training on the operation of the developed techniques is also conducted.
◎ Related facilities

Waste sampling at Fukushima Daiichi NPP site

Analyzing for tritium
This R&D contributes to part of the "Mid-and-Long-Term Roadmap towards the Decommissioning of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Units 1-4".
- (3-2) Development of Technologies for the Processing and Disposal of Radioactive Waste







