JAEA's Vision Future image
JAEA aims for a sustainable future society realized through the synergetic effect of nuclear and renewable energies.
JAEA strives to realize a decarbonized society by integrating nuclear and renewable energies. To this end, we structure our initiatives around three pillars, “Synergy”, “Sustainable”, and “Ubiquitous”, to support the transition to a carbon-neutral, resource -efficient society and contribute to human society.

- Pursuing Synergy of Nuclear and Renewable Energies
- Making Nuclear Technology Ubiquitous
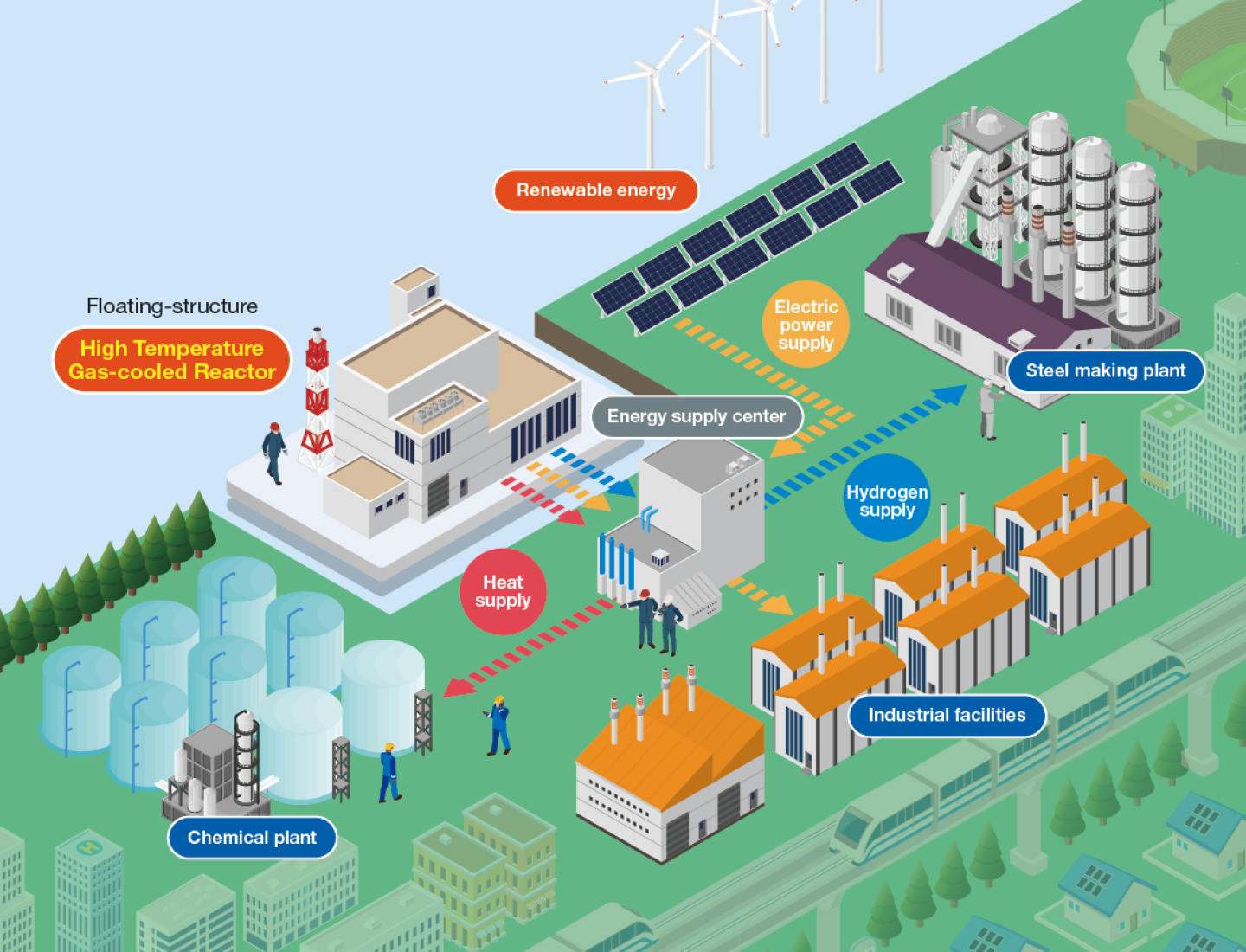
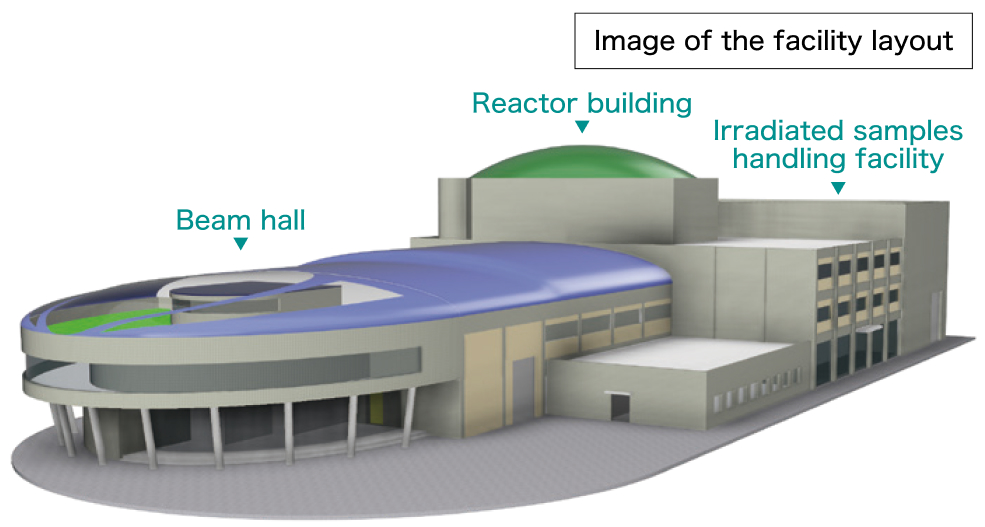
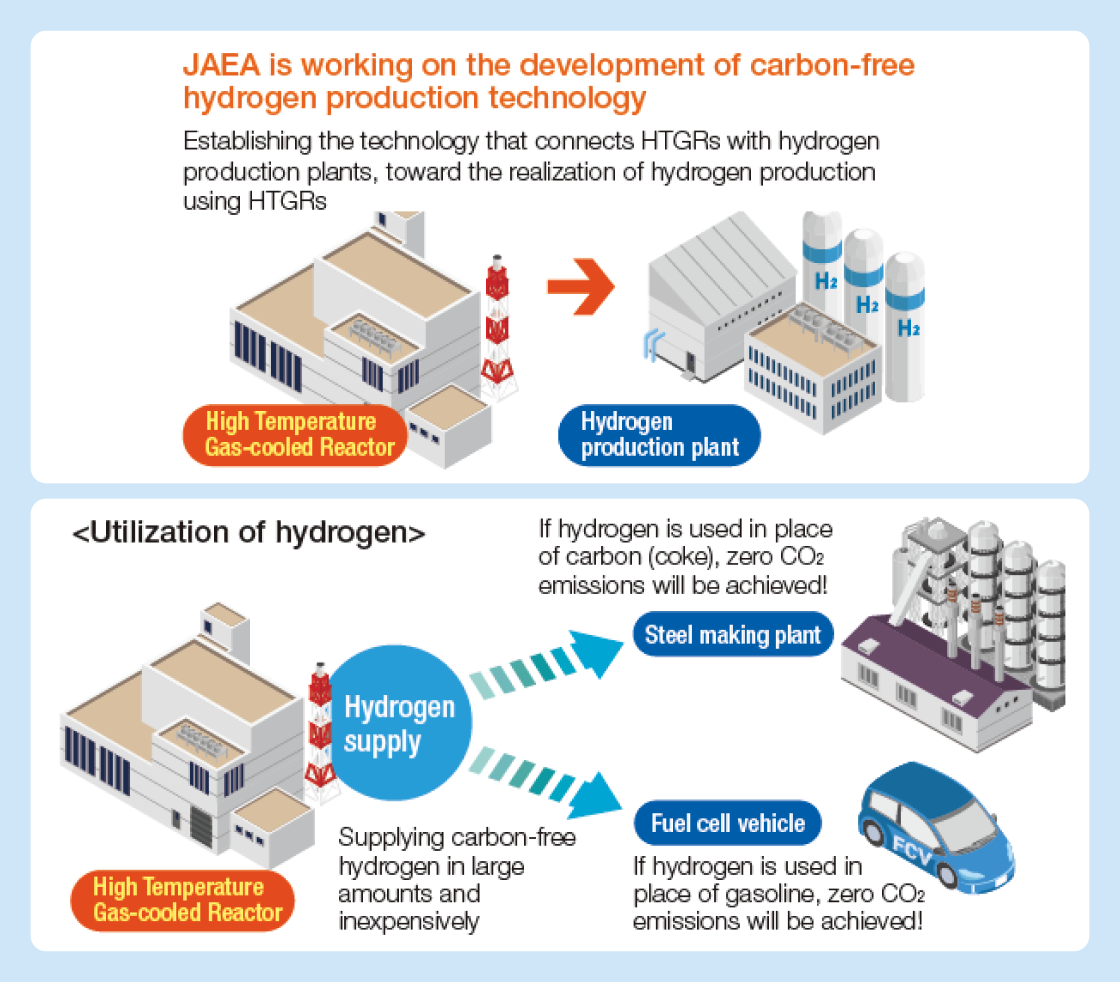
“Development of a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor contributing
to the realization of a decarbonized society by 2050”
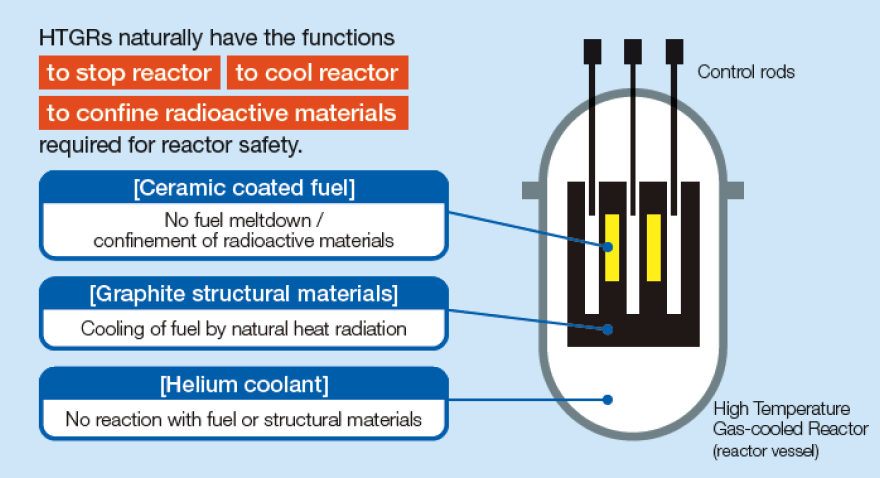
Development of HTGR
- Pursuing Synergy of Nuclear and Renewable Energies
- Making Nuclear Energy Sustainable
- Making Nuclear Technology Ubiquitous
“Reduction and recycling of high-level radioactive wastes,
enabling domestic medical isotope production”
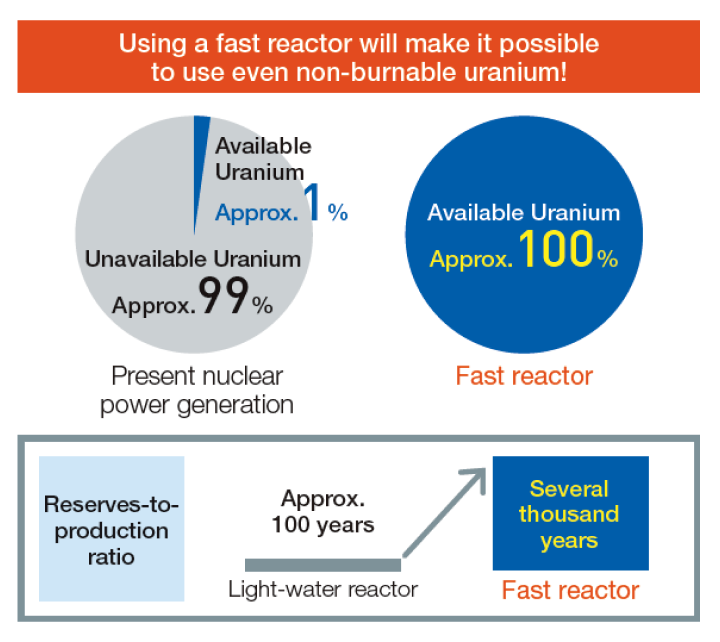
Development of Fast Reactor

- Pursuing Synergy of Nuclear and Renewable Energies
- Making Nuclear Energy Sustainable
- Making Nuclear Technology Ubiquitous
“Maximizing the use of non-burnable uranium and
radioactive waste from nuclear energy
generation”
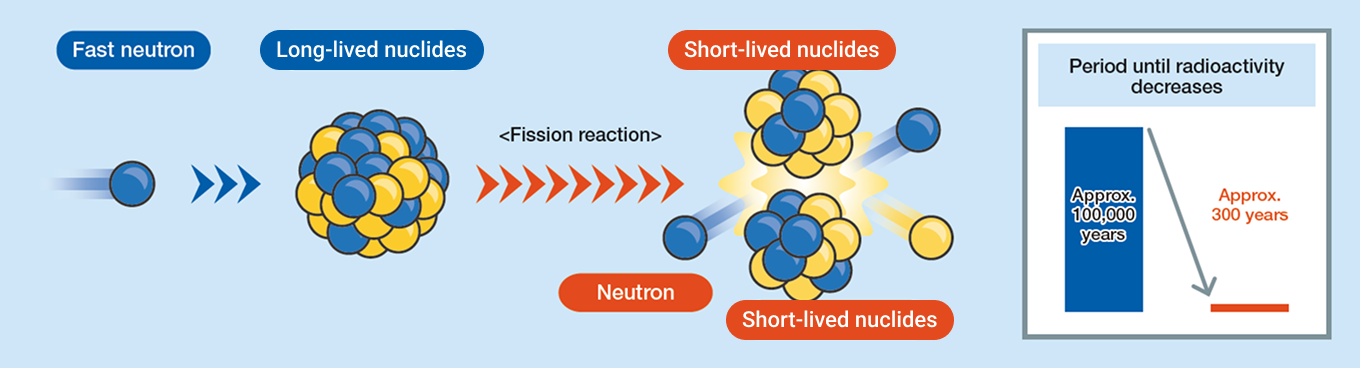
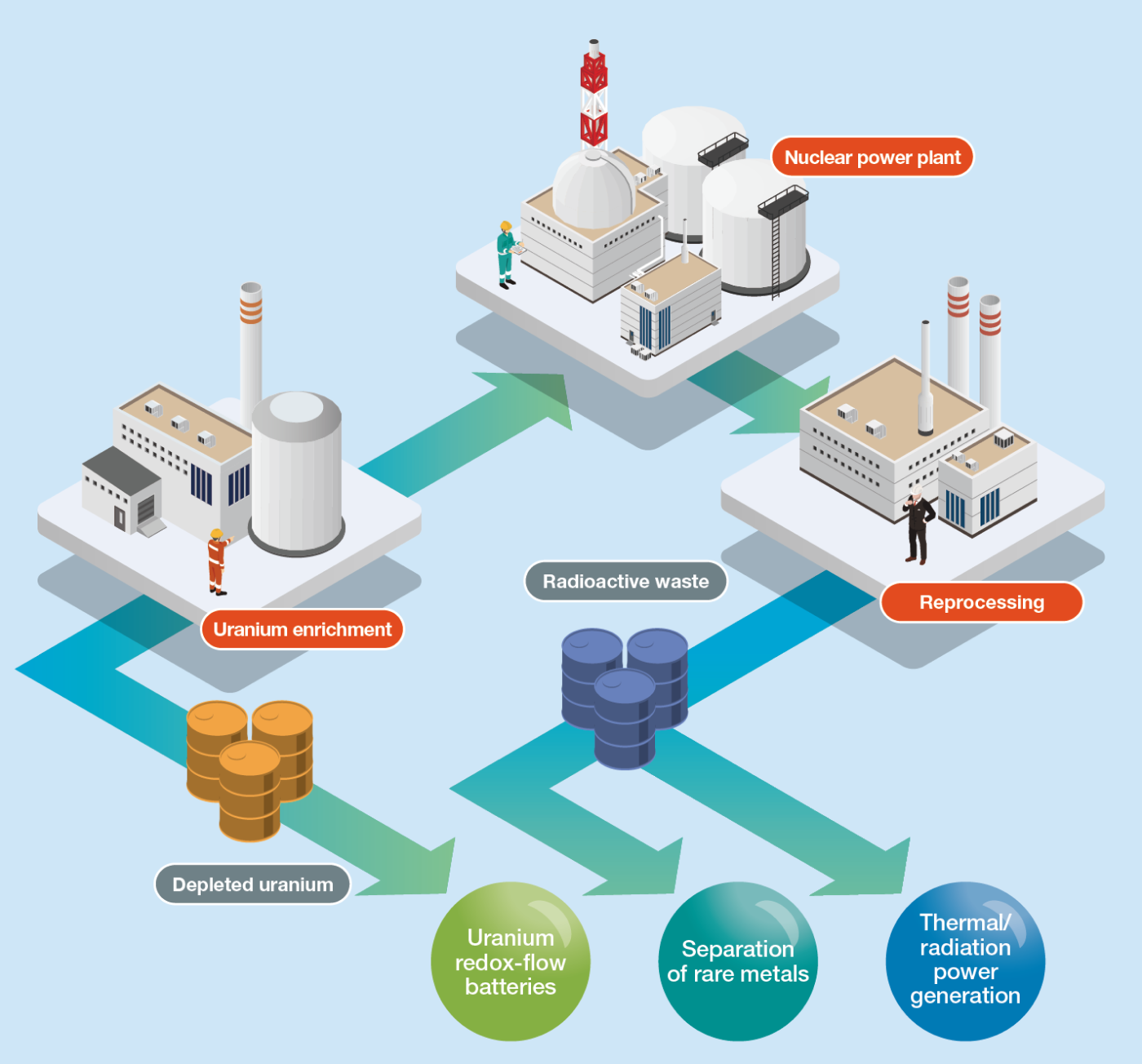
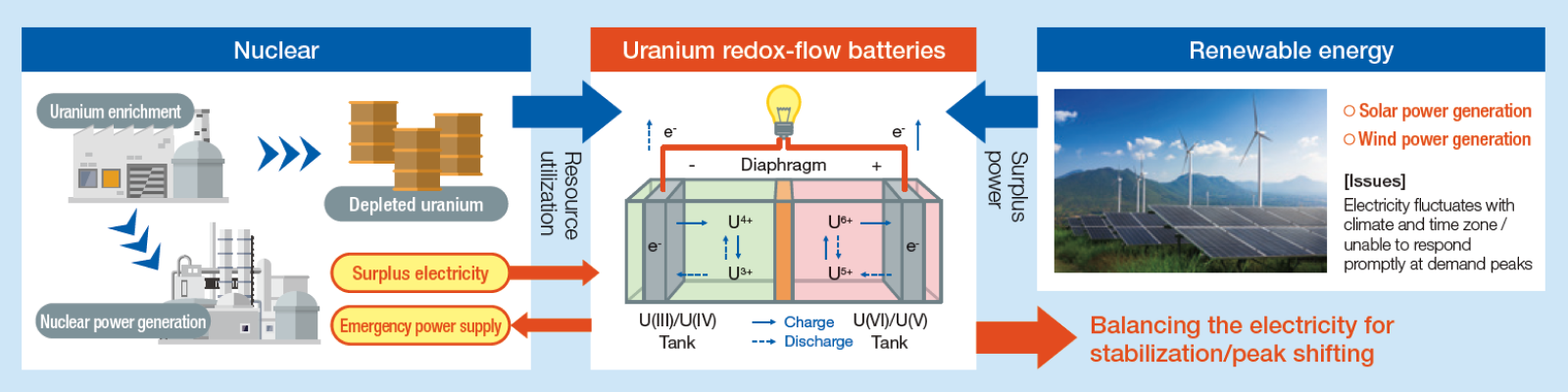
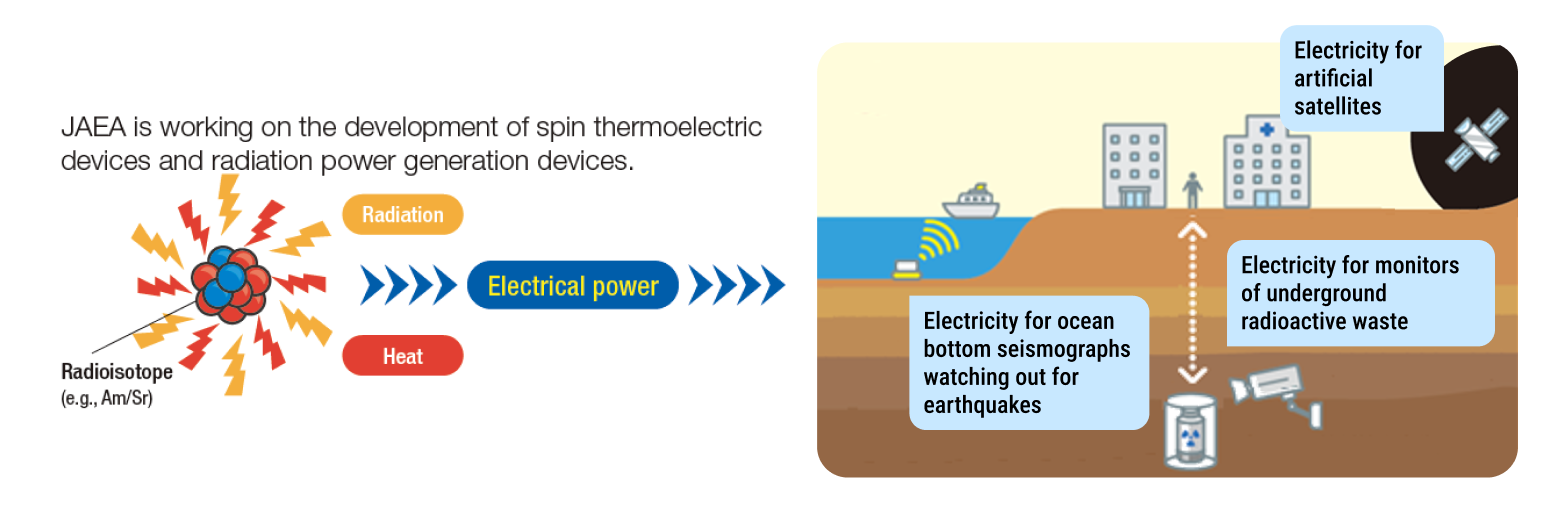
Recovering Valuable Resources from Radioactive Waste
- Making Nuclear Energy Sustainable
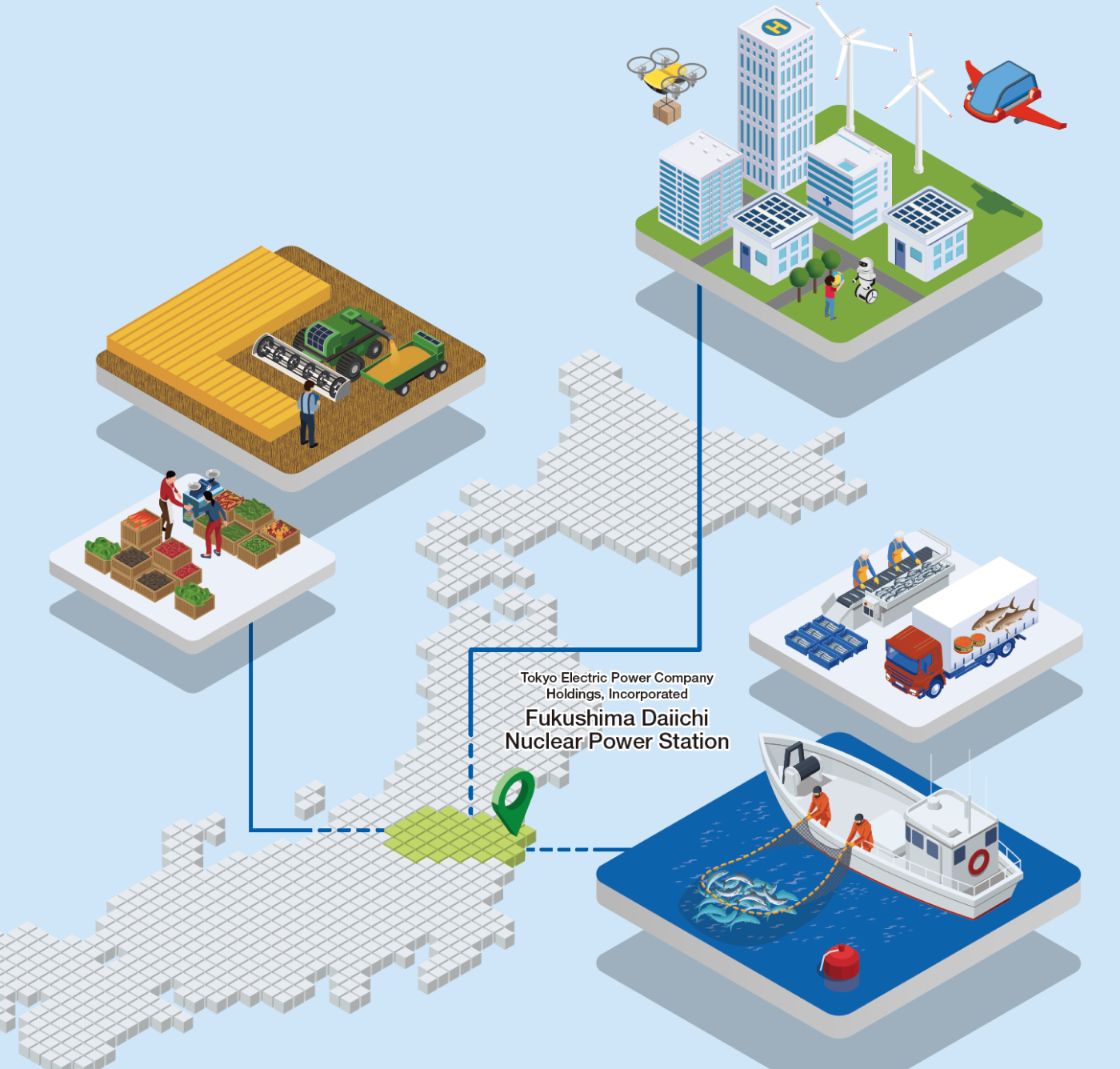
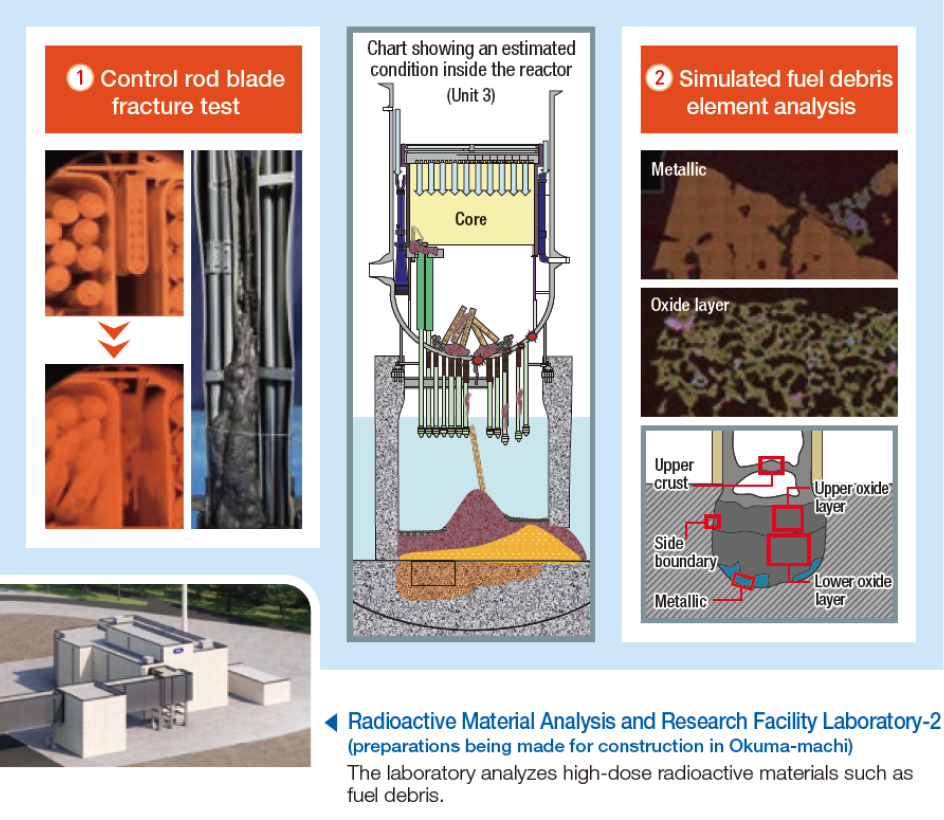
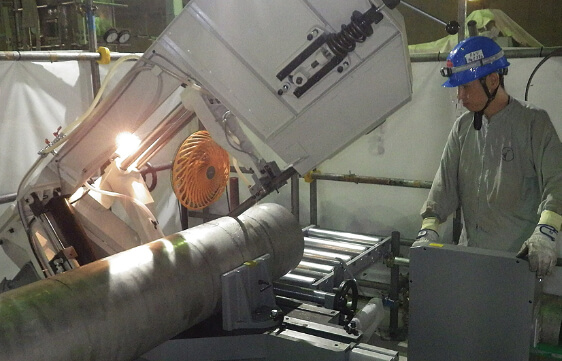
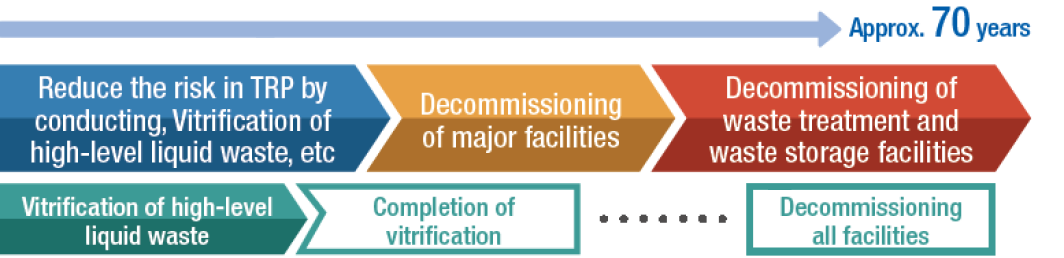
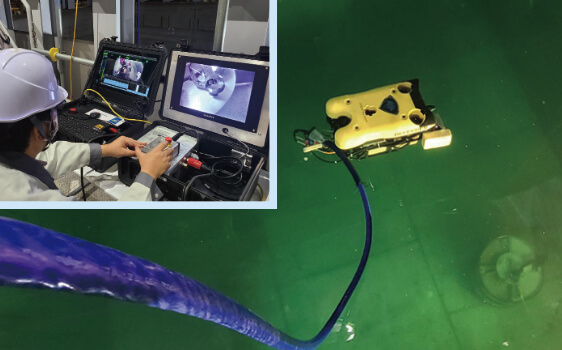
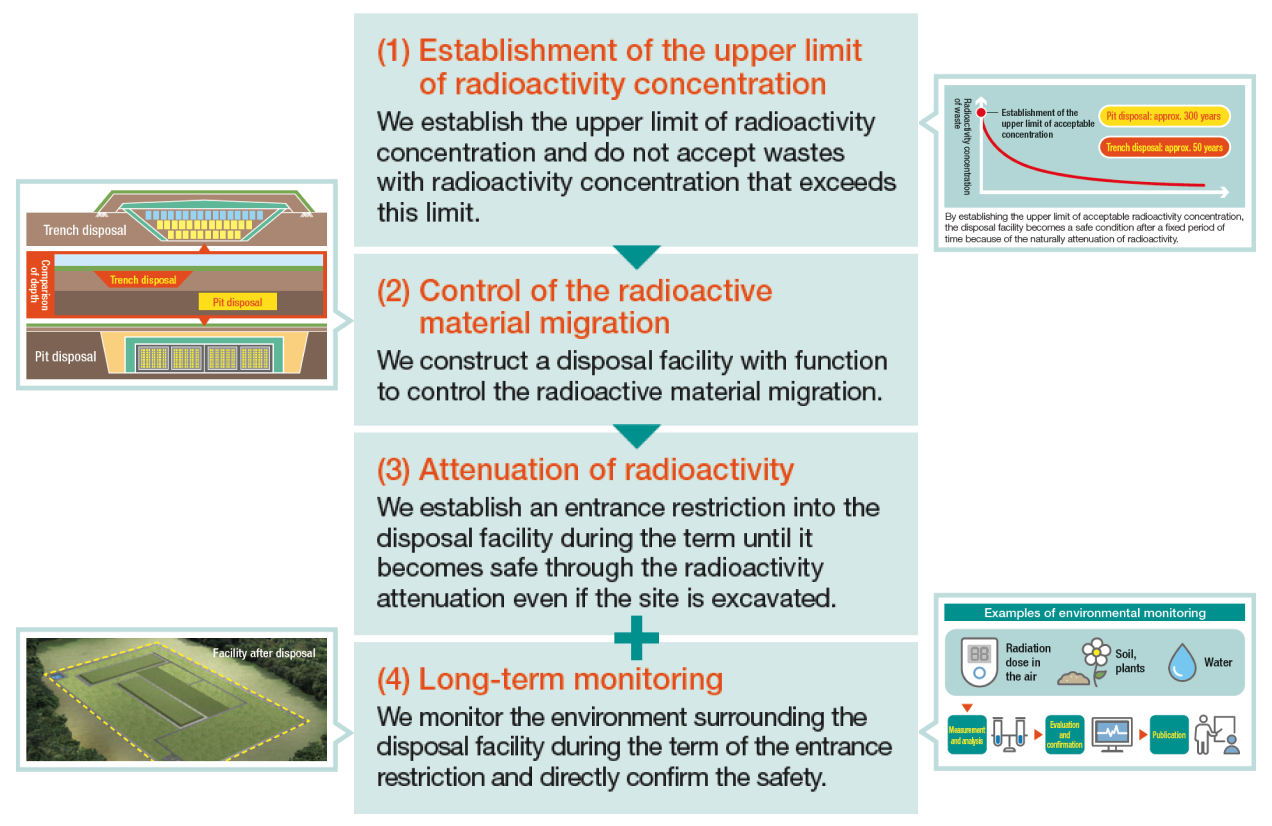
“Support for decommissioning and environmental restoration
at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F)”
Support for Decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and Efforts Toward Environmental Restoration

- Making Nuclear Energy Sustainable
- Making Nuclear Technology Ubiquitous
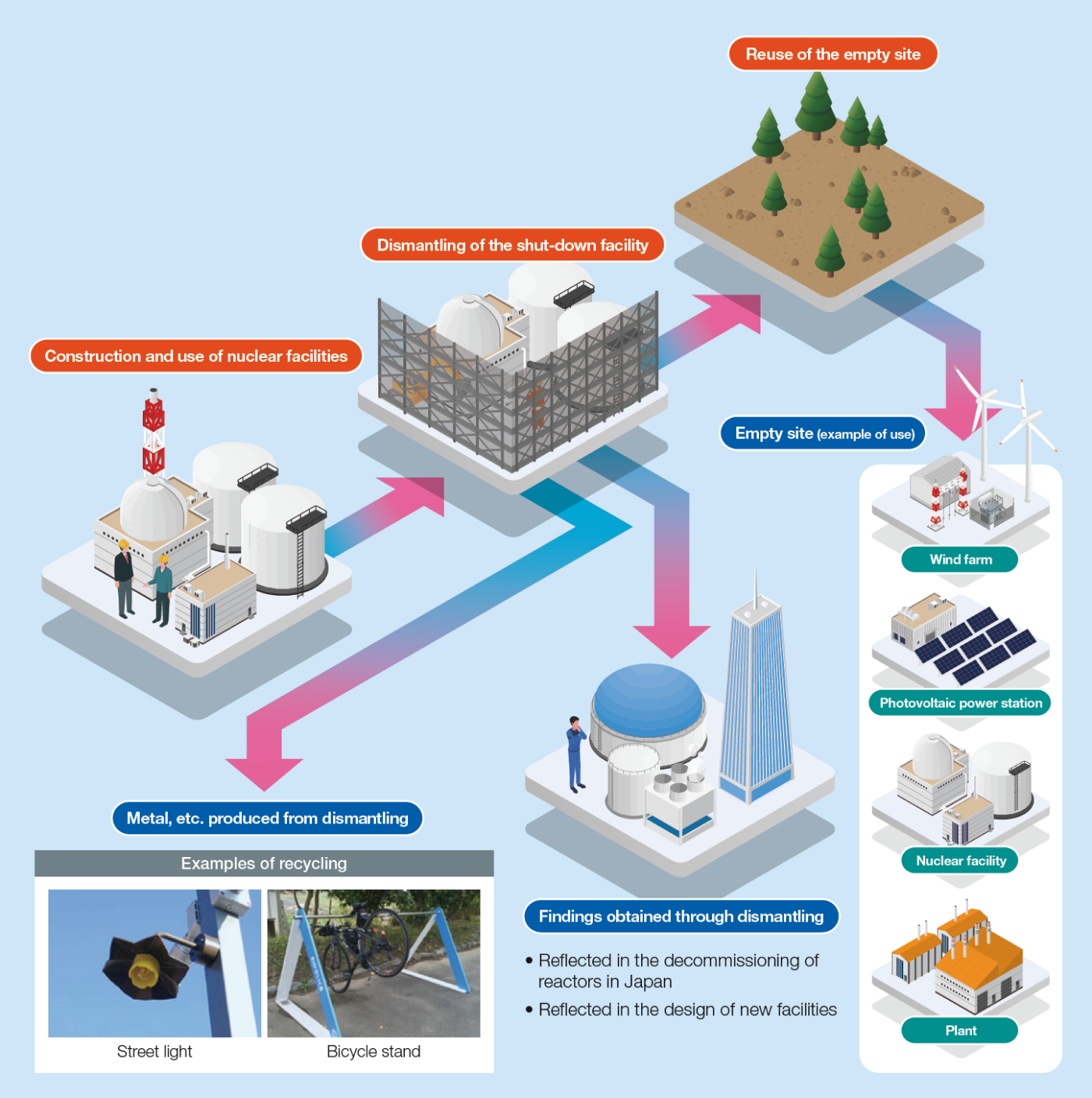
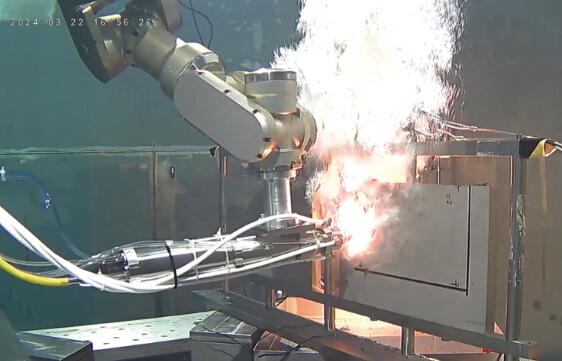
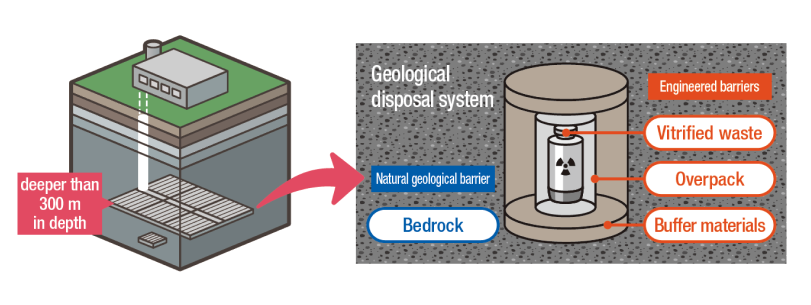
“Establishing a sustainable life cycle for nuclear facilities”
Consolidating findings on nuclear facility decommissioning technologies
- Pursuing Synergy of Nuclear and Renewable Energies
- Making Nuclear Energy Sustainable
- Making Nuclear Technology Ubiquitous
Other initiatives
Domestic medical isotope production
AEA is advancing research and development to domestically produce medical isotopes for cancer treatment and diagnostic imaging.
- Pursuing Synergy of Nuclear and Renewable Energies
- Making Nuclear Energy Sustainable
- Making Nuclear Technology Ubiquitous
Other initiatives


smartphones, etc.
Example of application overseas
The tumor in the late-stage metastatic prostate cancer has
completely disappeared!
(all signs of cancer disappeared)
The administration of actinium-225 to a patient with cancer that had spread throughout the body resulted in the disappearance of the cancerous tumors.
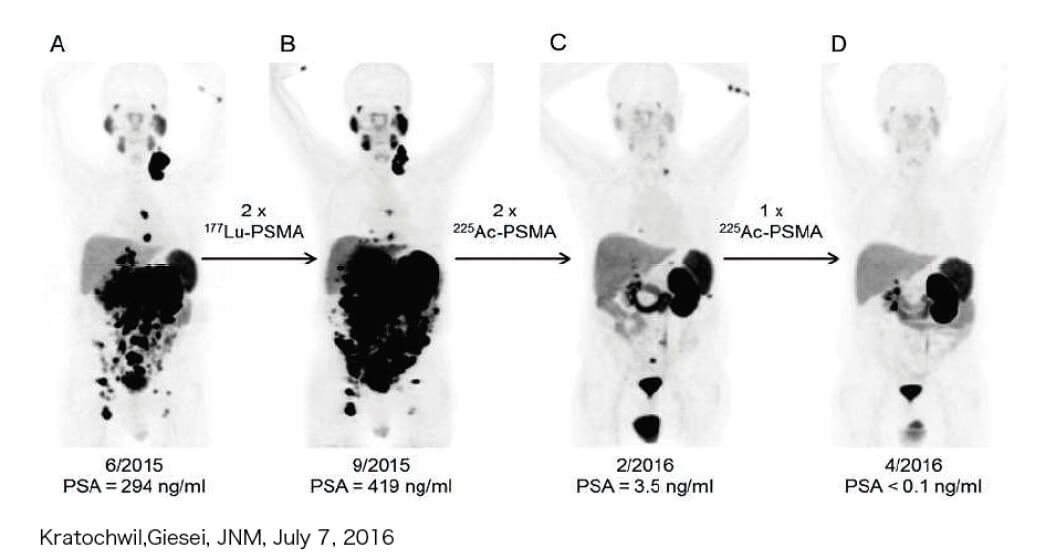
Killing cancer cells with actinium 225 radiation
Example of achievement
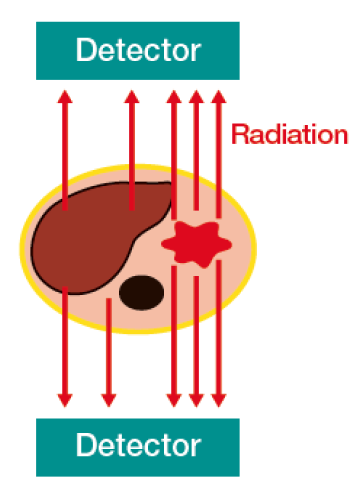
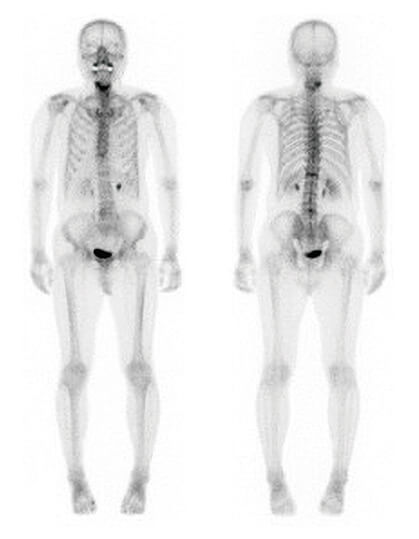
Early diagnosis with less impact on the body!
Bone scintigraphy is known as one of the most frequently conducted tests among nuclear medicine examinations.
- [Advantages]
-
- Functional diagnostic imaging that reflects changes in bone metabolism
- Systemic search is easy (figure on the right)
- Effective for judging the effect after treatment, and in follow-up
Example of bone scintigraphy
Website of the Nuclear Medicine, Center hospital of the National
Center for Global Health and Medicine
(https//www.hosp.ncgm.go.jp/s037/010/080/010/index.html)