Development of irradiation technology for large-diameter NTD Silicon
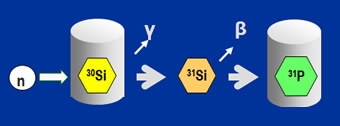
Principles of NTD method
Neutron transmutation doping (NTD) is used to dope silicon by transmuting silicon atoms (30Si) into phosphorous atoms (31P) through the following reaction
30Si(n,γ)31Si → 31P + ß– .
Advantage to NTD method
Since NTD is superior in homogeneous doping, NTD silicon has been widely used for the manufacture of high-quality semiconductors for use in high-voltage devices
Application of NTD silicon semiconductor
NTD silicon has been widely used for the manufacture of high-quality semiconductors for use in high-voltage devices such as electric trains.
Current state of NTD technology
To increase the amount of neutron-transmutation-doped silicon (NTD-Si) produced, it is essential to irradiate large-diameter silicon ingots.(Currently, NTD-Si ingots are 6 inches in diameter).
NTD technology challenge
Since the neutron flux at the periphery of silicon is greater than that at its interior,
irradiation cannot produce homogeneous results.
Solution to the challenge:
A thermal neutron filter has been designed and produced to decrease the thermal neutron intensity around silicon. As epithermal neutrons were introduced into the silicon ingot, the epithermal neutrons were moderated by silicon itself, producing thermal neutrons inside silicon. To homogenize the distribution of the thermal neutrons in silicon ingots, an irradiation method has been developed to produce high-quality 12-inch-diameter silicon semiconductors.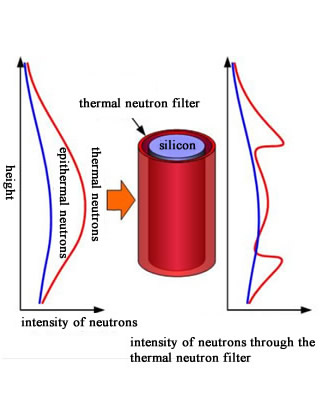
Conceptual diagram of using a thermal neutron filter to improvement the radial distribution of thermal neutron flux
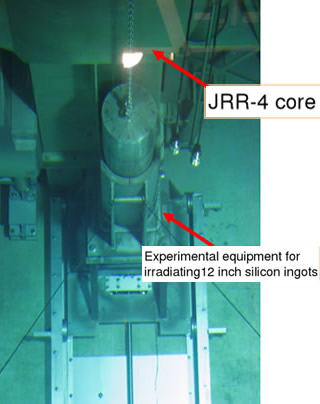
Equipment installed in JRR-4 for 12-inch NTD-Si irradiation experiments with a thermal neutron filter







