|

Demonstration of Shotcrete Construction in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Using Low Alkaline Cement
-Development of New Technology for Safe HLW Waste Disposal-
Oct. 15, 2009
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been developing low alkaline cement as part of research and development of high level radioactive waste disposal. In the year 2009, JAEA has succeeded the full-scale shotcrete construction in the Horonobe underground research laboratory (URL) using the low alkaline cement for the first time in the world.
The new technology which JAEA has demonstrated in the Horonobe URL in this year can ensure the applicability/availability for the shotcrete construction with the newly developed low alkaline cement (HFSC: Highly Fly-ash contained Silica-fume cement) and enhance the long term safety of the geological disposal. Thus, the low alkaline cement is expected to be applied not only for the geological disposal but also for civil engineering work such as constructions of generic waste disposal facility, embankments of rivers.
In constructing shafts and horizontal drifts of the Horonobe URL, the concrete material is usually used as mechanical support system for ensuring the tunnel stability. The support system is indispensable in the construction of tunnels in the soft sedimentary formations. Although the pH of the groundwater sampled from deep borehole investigations carried out from the ground surface is raging from 6 and 9, the ordinary Portland cement, which is a main composite of the concrete material used for the support system in tunneling, generates high alkaline plume (the pH is usually higher than 12.5) by contacting with surrounding groundwater. The high pH plume could negatively affect the long term stability of the multi-barriers for the HLW disposal system and reduce the barrier performance. In order to reduce such influence due to the high pH plume and to ensure the long-term safety for the geological disposal, JAEA has been developing the low alkaline cement, HFSC in which silica fume and fly ash are mixed with OPC. The low alkaline cement has also been aggressively developed in European countries such as Switzerland, Finland and Sweden. In these countries, in-situ tests of the low alkaline cement using the small portion of tunnel were carried out. JAEA has been preparing the full-scale demonstration of shotcrete construction with the HFSC in the Horonobe URL by carrying out the exchange of information with these countries through the collaboration.
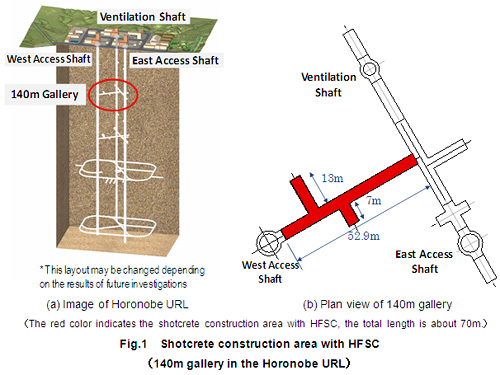
JAEA has confirmed the applicability/availability of the HFSC by constructing the shotcrete with the HFSC at the 140m gallery which was constructed at the depth of GL -140m in the Horonobe URL (see Fig. 1) in the year 2009. Total length of the shotcrete construction is about 70m, total shotcrete area is about 930m2, and total volume of the shotcrete utilized is 500m3 (see Photo 1 & 2). As a result, the shotcrete with HFSC was proved to have similar applicability/availability with the OPC which are usually utilized in civil engineering works. In addition, mechanical stability, such as convergence, of the HFSC showed the similar performance with the OPC. Therefore, the shotcrete construction with HFSC was confirmed to be applicable and available in the underground facilities such as Horonobe URL. The full-scale shotcrete construction with the low alkaline cement (HFSC) in an actual underground facilities and the confirmation of the practical use carried out by JAEA are the first time in the world.
As a future work, change of the pH in the surrounding groundwater and the influence of the surrounding rocks due to the pH from the shotcrete constructed at the 140m gallery of the Horonobe URL are planned to be continuously investigated.

|

Location of environment monitoring posts measuring amount of
radiation. (details)

International link directory of related websites.
|
