|
Supplementary document 1. Background (1) Ionic liquids Ionic liquids are ambient temperature molten salts. Typical ionic liquids are composed of an organic cation (imidazolium, pyridinium, ammonium, etc.) and an anion (Cl-, BF4-, PF6-, (CF3SO2)2N-, etc.). Innumerable combination of a cation and an anion enables synthesis of a large variety of ionic liquids (Figure 1). 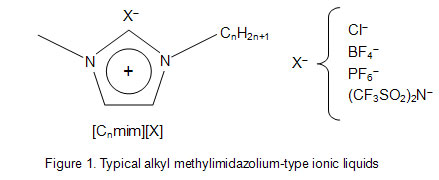 Properties of ionic liquids are as follows. (i) Negligible vapor pressure (ii) Nonflammability and high thermal stability (iii) The chemical and physical properties (density, polarity, hydrophobicity, viscosity, etc.) are effectively tunable by altering the cation and the anion. Specifically, ionic liquids, which have high polarity but are immiscible in water and organic solvents, are able to be synthesized. (iv) Relatively high ion conductivity Ionic liquids are expected as green solvents by the features of (i) and (ii), and have been applied to environmental protection processes in various fields. As shown in the features of (iii) and (iv), ionic liquids have great potential as unprecedented reaction media because they provide unique environments different from those in water and organic solvents. Ionic liquids have been receiving great expectation in expansion of the frontiers. (2) Background on solvent extraction utilizing ionic liquids - challenge to extracting biomolecules - Solvent extraction is separation and concentration techniques utilizing the difference of distribution behavior between aqueous solution and organic solution. By contacting an organic solution containing an extractant with an aqueous solution containing target substances, extractable substances are selectively transferred into the organic solution with unextractable substances remaining in the aqueous solution. Conventional solvent extraction uses organic solvents, which are flammable, volatile, and usually toxic. From the viewpoint of environmental protection, the use of such hazardous solvents is unfavorable. To address this issue, ionic liquids are receiving much interest as alternative media to conventional organic solvents. Ionic liquids show remarkably high extraction performance compared to conventional organic solvents. However, there is no study showing effective extraction of proteins, although metal ions and simple organic compounds have been chosen as extraction targets. (3) Background on ionic liquid as reaction media for biocatalysis Enzymes act as biocatalysts in vivo, and are essential proteins to support life. Enzymes inherently fulfill their functions in water. In 2000, however, it was reported that enzymes can also provide their activity as heterogeneous catalysts in ionic liquids. Since proteins are usually insoluble in ionic liquids, the suspended condition leads to decline in their enzymatic activity. Thus, it is very important to directly solubilize proteins in ionic liquids while still maintaining their functions. Furthermore, unique features of ionic liquids might convert functions of proteins. 2. Results and discussion (1) Extraction of biomolecule into ionic liquids We employed an ionic liquid incorporating hydroxyl group, which is expected to provide high affinity for proteins, in order to achieve quantitative extraction of proteins. The ionic liquid dissolving a macrocyclic compound crown ether, which interacts with proteins, was mixed with an aqueous solution containing a heme protein cytochrome c. As shown in Figure 2, cytochrome c (red color) was quantitatively extracted from the aqueous phase (upper phase) into the ionic liquid phase (lower phase) through formation of a supramolecular complex with crown ether. 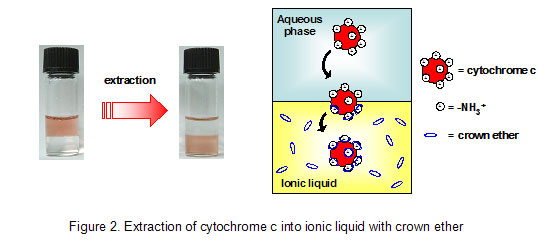 (2) Functional conversion of cytochrome c to peroxidase As mentioned above, we have achieved solubilization of cytochrome c in an ionic liquid through solvent extraction technique. Furthermore, it has been found that cytochrome c in the ionic liquid provides a new functionality as peroxidase. As shown in Figure 3, cytochrome c in water displays minor peroxidase activity in the oxidation reaction of 2,6-dimethoxyphenol (2,6-DMP). On the other hand, cytochrome c in the ionic liquid offers high peroxidase activity, and accelerates the oxidation reaction rate, which is attributed to the structural change of the heme vicinity of cytochrome c in the ionic liquid. 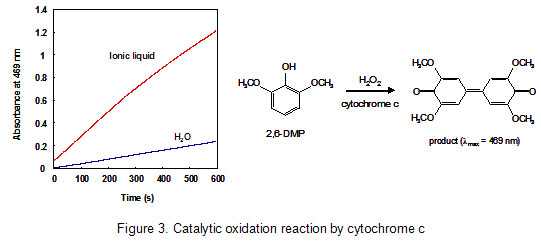 3. Significance and spin-off (1) Application of ionic liquids to extracting media of biomolecules The use of proteins in ionic liquids is problematic in that proteins are usually insoluble in ionic liquids. This is the first study showing the extractive solubilization of a protein in ionic liquids, which addresses the issue on solubility of proteins in ionic liquids. This technique is applicable to separation technology of proteins, since specific proteins are selectively transferred into ionic liquids. In the future, ionic liquids will be applied to not only extracting media but also reaction media of proteins. (2) Functionalization of proteins in ionic liquids The use of proteins in ionic liquids enables the biocatalytic reaction which cannot proceed in water. Specifically, it is expected that ionic liquids are applied to the biodegradation of environmental pollutants (endocrine disrupter, pesticide, etc.), which are insoluble in water. In addition, unique features of ionic liquids might convert the intrinsic functions of proteins. ( BACK ) |



