|

Attachment 1
Release a Statement of Expressions of Interest to Technological Proposals on the Global Nuclear Energy Partnership (GNEP)
September 8, 2006
Japan Atomic Energy Agency
The Department of Energy (DOE) in the United States, this past February, announced the comprehensive concept, so called GNEP, aiming at a nuclear expansion, a reduction of radioactive wastes and a completion of non-proliferation (*1). Thereafter, on August 3, DOE announced that it is considering a two-track approach (*2) to accelerate the GNEP program, and seeking expressions of interest (EOI) to obtain input from U.S. and international nuclear industry to accelerate development and deployment of advanced recycling technologies for proceeding with commercial scale demonstration facilities, specifically a Consolidated Fuel Treatment Facility (CFTC) and an Advanced Burner Reactor (ABR). Abstract of requests for EOI is as follows:
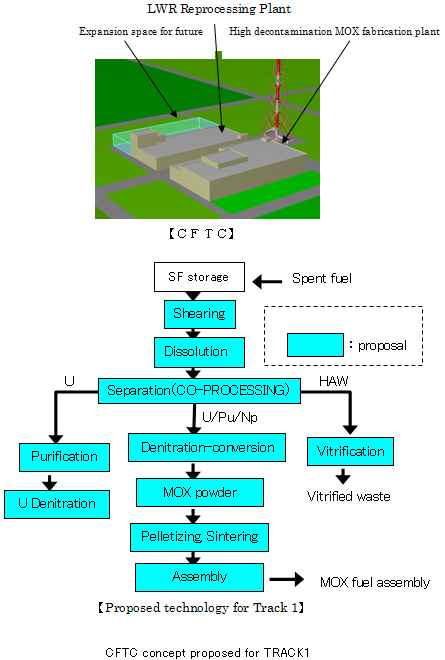
CFTC:
To avoid the emergence of pure plutonium
| (1) |
Near-term Track (Track 1) : Assumed reprocessing capacity is several hundreds t/year, and spent light water reactor (LWR) fuel will be reprocessed for use in fabricating ABR driver fuel (not containing Minor Actinides (MA) for a while). |
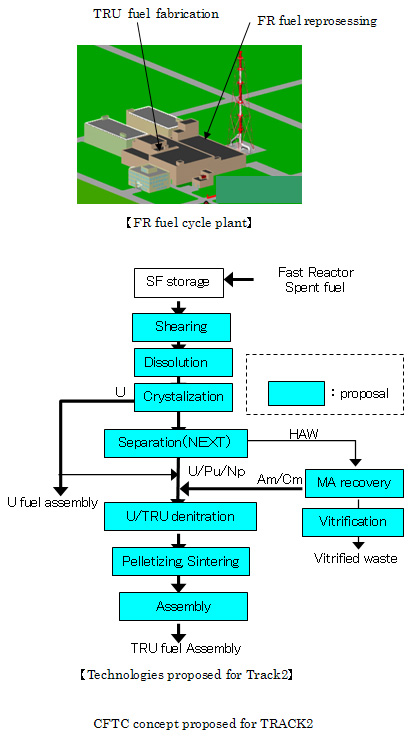
| (2) |
Long-term Track (Track 2) : Spent fuel from fast reactors will also be reprocessed for use in fabricating ABR fuel (containing MA). |
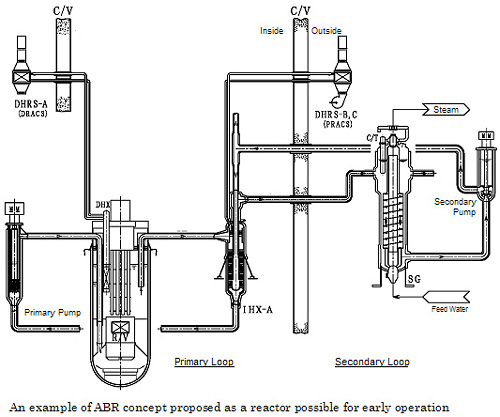
ABR:
Fast neutron reactor, and its output is assumed 500-2000 MWt, 200-800MWe. The ABR will start with conventional fast reactor fuel, subsequently would be used to demonstrate the feasibility of recycling fast reactor transmutation fuel. Sodium Cooled Fast Reactor is given as an example.
The proposal for EOI , with JAEA and related manufactures so on, is made based on the abundant experience of construction and operation of experimental reactor JOYO and prototype MONJU as well as design study of Demonstration Fast Reactor and Feasibility Study of Commercialization of Fast Reactor since 1999 (FS).
CFTC:
| (1) |
Near-term Track (Track 1) : Assumed start operation is around 2020, proposed system focuses on the modification of technologies based on abundant design/construction/operation experience in Japan. |
| (2) |
Long-term Track (Track 2) : Assumed start operation is around 2030-2040, proposed system focuses on the innovative technologies developed in FS in Japan. |
ABR:
DOE expects to commence ABR around 2020, therefore proposed design is that some parts of innovative technologies to be adopted in the Japanese demonstration fast reactor to commence around 2025, are displaced to the existing technologies (*3) .
(*1) GNEP (Global Nuclear Energy Partnership)
As part of President Bush’s Advanced Energy Initiative, February 6, 2006, DOE announced the GNEP, which is the comprehensive concept for expanding nuclear without greenhouse gasses by recycling nuclear fuels, demonstrating & arranging the new technologies to minimize radioactive wastes, and promoting non-proliferation. The GNEP includes 7 elements.
| 1. |
Build new generation nuclear power plants in U.S. |
| 2. |
Demonstrate & arrange the new nuclear fuel recycle technologies |
| 3. |
Manage spent fuels effectively in U.S. and deposit them in U.S. |
| 4. |
Develop the ABR which produces energy from recycled nuclear fuels |
| 5. |
Establish the fuel supply service program that developing nations can operate the nuclear power plants, minimizing the proliferation risk |
| 6. |
Develop & build the small reactor well-suited to conditions in developing nations |
| 7. |
Modify safeguards to enhance proliferation resistance and safety of expanded nuclear power plants |
(*2) two-track approach
| (1) |
Track 1 : Near-term Track : It is to separate the usable uranium and transuranics from spent light water reactor fuel for use in fabricating fast reactor fuel, is aiming to operate early utilizing ordinary technologies. |
| (2) |
Track 2 : Long-term Track : It is to separate the usable uranium, minor actinides (MA), and transuranics (except MA) from spent light water reactor fuel for use in fabricating fast reactor fuel. It is to separate and fabricate fast reactor transmutation fuel. For developing those technologies it takes a long time. |
By utilizing these two Tracks together and operating a facility early in a short term, reduction of radioactive waste and MA burning which are the final objectives would be accomplished, and possibilities to the closed fuel cycle could be realized.
(*3) design is that some parts of innovative technologies are displaced to the existing technologies
Double-wall-straight-tube SG are displaced to single-wall-herical-tube SG or single-wall-straight-tube SG, and integrated IHX and pump are separated IHX and pump, and so on.
 Back to the article Back to the article
|

Location of environment monitoring posts measuring amount of
radiation. (details)

International link directory of related websites.
|







