|
Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory Project
Results from 1996-1999 Period
|
| 4. Main results of the Phase I-a |
| 4.4 Rock mechanical investigations |
Based on a comprehensive assessment of the results of physical/mechanical property tests and initial stress measurements in the AN-1, MIU-1 3, a rock mechanics conceputual model from the ground surface to 1,000m in depth is constructed. The model is shown in Fig.4.70. Its characteristics is as follows.
3, a rock mechanics conceputual model from the ground surface to 1,000m in depth is constructed. The model is shown in Fig.4.70. Its characteristics is as follows.
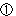 The rock mass on the hanging wall side of the fault is divided into three zones characterized by different physical/mechanical properties and stress states. Specifically, Zones-1, 2 and 3 range in 0
The rock mass on the hanging wall side of the fault is divided into three zones characterized by different physical/mechanical properties and stress states. Specifically, Zones-1, 2 and 3 range in 0 300/400m, 300/400
300/400m, 300/400 700m and 700
700m and 700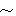 1,000m, respectively.
1,000m, respectively.
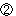 The investigation results of the rock mass on the footwall side are restricted to 150
The investigation results of the rock mass on the footwall side are restricted to 150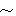 200m and 800
200m and 800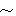 1,000m in depth. Therefore, the whole side is assumed to consist of the homogeneous rock mass. It is difficult at the moment to estimate the position and extension of fault-related and fracture-concentrated zones as those recognized in the DH-9. Therefore, the whole section is postulated to consist only of sound rocks without above-mentioned zones.
1,000m in depth. Therefore, the whole side is assumed to consist of the homogeneous rock mass. It is difficult at the moment to estimate the position and extension of fault-related and fracture-concentrated zones as those recognized in the DH-9. Therefore, the whole section is postulated to consist only of sound rocks without above-mentioned zones.
Though the rock mechanics conceptual model is revised by adding the data of mechanical properties of the footwall, the basic concept of the model is same between before and after the revision. In this concept, the rock masses on the footwall side and the hanging wall side show mechanically discontinuous behaviors. Furthermore, the hanging wall side of the Tsukiyoshi Fault is obliquely pressed against the footwall side by the regional tectonic stress. This hypothesis requires that the rock mass on the hanging wall side is divided into blocks bordered by N-S trending faults besides the E-W trending Tsukiyoshi Fault. N-S trending lineaments are identified by lineament surveys carried out in and around the Shobasama site for the RHS Project are thought to support the above-mentioned hypothesis.