The source of radiation exposure during maintenance work at a nuclear power plant is radioactive metallic oxides, commonly called "crud," which deposit and pile up on the surface of equipment and piping. As a measure of reducing exposure, water chemistry control, e.g. suppression of crud generation and its adhesion to the surface of equipment and piping, or chemical removal of crud layer, is more effective than physical countermeasures like shielding. The development and advancement of technologies for water chemical countermeasures have been pursued at Fugen for many years. Finally technology combined chemical decontamination and zinc injection, considered as a permanent measure, was established at Fugen.
For the first time at a nuclear power plant in service in Japan, chemical decontamination was applied to the entire reactor coolant system by the use of chelate based diluted decontamination agent during the 8th (1991) and the 9th (1993) periodical inspections, which successfully achieved approximately seven to eight man・Sv, reduction of radiation exposure respectively. As well as development of the decontamination agent, careful studies were made on obtaining optimum conditions, estimating the effects of material composing the system, and designing a heat-up system used an actual heat exchanger.
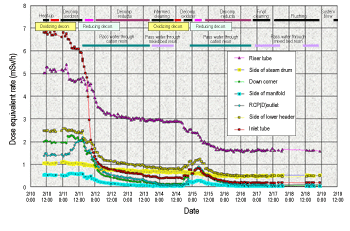
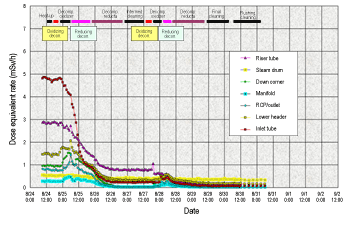
Later, due to the chemical composition change of the crud layer under the influence of long-term hydrogen injection, Fugen embarked on further development of chemical decontamination for plants employing long-term hydrogen injections. An operational compatibility test of the new decontamination method, redox decontamination (the HOP method), was carried out in order to verify the effectiveness of its use in Fugen. In the HOP method, one basic decontamination cycle consists of two steps: oxidizing decontamination used potassium permanganate as the agent, and deoxidizing decontamination used oxalic acid andhydrazine. Its advantage is that the decontamination process conditions, including the concentration of the agent, the duration of the steps, and the number of cycles, can be adjusted according to the crud properties and targeted decontamination factor. |
|
| Schematic Diagram Illustrating Dissolution of Fixed Oxides by Redox Decontamination (HOP) |
|